Overview of SC Modeler 4.1
|
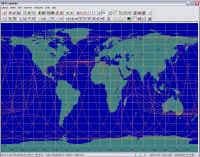
The SC Modeler software is a comprehensive tool for the conceptual design, visualization, and analysis of satellite networks, ranging from small groups of interconnected satellites to extensive multi-layered satellite constellations. It provides an integrated modeling environment and essential functionality that enables rapid development, visualization, and analysis of satellite constellation design alternatives, facilitating performance comparison of satellite network variants at the architectural level. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SC Modeler comes with multiple options for designing new satellite constellations or defining the orbital parameters of existing ones:
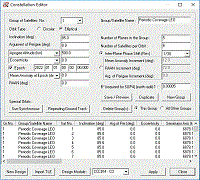
SC Modeler includes the Two-Body Keplerian, J2 Perturbations (no drag effects), and SGP4/SDP4 orbit propagators. (more) Users can create static or animated 2D or 3D views of the constellation and interactively examine it by adjusting the azimuth and elevation of the viewpoint, rotating or moving the view, moving the ground stations, and zooming in or out. The viewpoint can be placed above a satellite or ground station. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
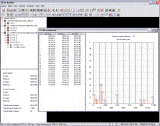
The software allows for the visualization and analysis of all intersatellite links, all communication links to a specific ground station or satellite, or a chain of communication links between any pair of network nodes: "ground station-ground station," "ground station-satellite," "satellite-satellite." SC Modeler employs a hierarchical routing algorithm that enables a fast and accurate search for the shortest path between the source node and the destination node in accordance with the chosen routing policy. This capability persists even for large, multi-layered mega-constellations comprising thousands of satellites. During simulations, either in "fast" or real-time mode, the program generates and continuously refreshes charts, histograms, and textual reports characterizing the network topology, route stability, properties of active communication links, and revisit characteristics. These include the number of potential connections available to a ground station or satellite, total path length (edges or km) and delay, route duration, length of uplinks, downlinks, and intersatellite links, intersatellite range rate and relative velocity, access intervals and service gaps, and more. The software also allows you to determine visibility intervals when the required number of satellites is available to a ground station or satellite. Historical data related to communication route changes can be collected and reviewed. The software includes a set of productivity tools that offers an efficient and convenient way of managing model properties, constellation parameters, and design constraints. The Access Constraints tool allows you to define one or multiple Earth observation sensors, uplinks, or downlinks with conic, rectangular, or custom field of view for a single satellite or a group of satellites. It enables you to establish access constraints specific to these components and specify the boresight orientation. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For intersatellite links, you can specify the minimum clearance above the Earth and the maximum propagation range. The total number of hops across the satellite for the whole path can be limited or set to 0, or intersatellite links can be disallowed. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For a constellation design, you can specify multiple variants of the network topology (this will require the Network Topology tool) and access constraints. You can save the related configuration parameters to an application-generated database. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The Session History tool allows you to navigate easily through constellation designs created during the current work session or those restored from a database. You can activate any available constellation by double-clicking the desired item. Once activated, the connectivity rules and access constraints associated with the selected constellation will be retrieved from the database, and the constellation image and analysis results will be refreshed instantly. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Data sets produced during analysis can be saved in a fixed-width file format, making it easy to import them into a spreadsheet or a database program for further research. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Add-On Modules |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The software features a collection of modules created to deliver efficient solutions for complex constellation design and analysis needs. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Constellation Design Modules The Continuous Coverage Constellation Design/Circular Orbits module allows you to consider symmetric constellations (known as "Walker delta" constellations) and "streets of coverage" constellations with polar or inclined orbits (examples). The Continuous Coverage Constellation Design/Advanced Options module generates kinematically regular patterns with circular or elliptical orbits where all orbits have the same altitude, inclination, and argument of perigee. The generated constellation design should ensure the continuous availability of a specified number of satellites above the region of interest (examples). The Continuous Coverage Constellation Design/Advanced Options Plus module provides all the capabilities of the Continuous Coverage Constellation Design/Advanced Options module. In addition, this module generates kinematically symmetric constellation design patterns, which, in certain cases, perform better than "streets of coverage" and "Walker delta" constellations (example). The Periodic Coverage Constellation Design/Circular Orbits module generates kinematically regular patterns with circular orbits ("Walker delta" constellations) that provide the required maximum revisit time for given latitude bounds (examples). Constellation Design modules can help you to minimize the number of satellites required by the constellation if orbital inclination and altitude are specified. Alternatively, you can minimize the altitude of orbit for a given number of satellites and the orbit inclination. Other inputs of the design task are:
|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Coverage Analysis Modules
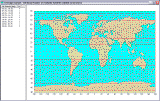
The Continuous Coverage Analysis module allows you to determine, for a given constellation, the minimum number of satellites that will be available at all times to each point at given latitudes. An analyzed constellation can include any combination of satellites or groups of satellites with the same orbit altitude and inclination. Each such subconstellation can be analyzed separately. You can specify individual access constraints for any group of satellites. The module generates the Coverage by Latitude tabular report and displays the results of analyses on a world map, with graphics depicting the various levels of coverage. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
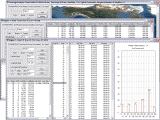
| The Periodic Coverage Analysis module allows you to undertake statistical analyses of visibility intervals for user-defined geographical regions. You can supply the exact locations of points and specify latitude bounds, or you can use the 2D map to define custom regions. The module determines visibility intervals for each point of the coverage grid and creates an interactive report that shows the revisit time (max/min, average), coverage time, number of gaps, and total coverage duration (%) measured over the entire simulation interval, etc. You can determine visibility intervals when the specified number of satellites is available to grid points. The results can be grouped by latitude and by region. The report includes a histogram showing the distribution of durations of visibility intervals (or gaps) for a selected set of points. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
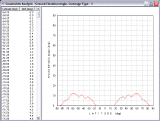
Constraints Analysis Module
The Constraints Analysis module allows you to determine latitude-dependent values of the minimum ground elevation angle, maximum satellite sensor's field-of-view, and maximum ground station to satellite propagation range, all of which have to be maintained by the generated constellation to provide the desired type of continuous coverage (single, double, triple, etc.) at specified latitudes. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Network Topology Tool
The Network Topology tool offers unmatched capabilities for configuring and manipulating the topology of a large satellite network. With this tool, you can create a set of connectivity rules by specifying combinations of the following parameters:
|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
If these connectivity rules cannot completely define the network structure, it can be configured further by activating or eliminating potential connections with the Matrix Editor. This interactive
tool displays the current connectivity matrix allowing you to manage (activate or eliminate)
network connections at various levels:
between two satellites, between subconstellations,
between satellites grouped in orbital planes, between satellites and
ground stations, etc. For any group of network connections, you can specify one or many time intervals during which the connections are active or inactive. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The routing algorithm supports four routing policies:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Interference Analysis of GSO and non-GSO satellites
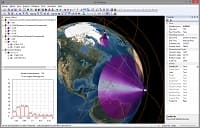
The Interference Analysis option evaluates the impact of operational restrictions, protecting the existing GSO (geostationary orbit) satellites from radio interference, on the coverage performance of a non-GSO constellation of communication satellites. The analysis is based on evaluating, at each time step, the separation (off-axis) angle - the angle between the line from the ground station to the GSO satellite and the line from the ground station to a non-GSO satellite. You can specify the minimum GSO separation angle constraint and position of GSO satellites and then use either the base product or the Periodic Coverage Analysis module to estimate the impact of the constraint on coverage statistics, including coverage gaps and accesses. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
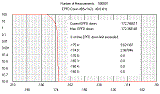
EPFD Analysis
The Equivalent Power Flux Density (EPFD) Analysis option allows you to determine the power levels produced by non-GSO fixed-satellite service (FSS) systems and use these results for examining non-GSO system compliance with the limits specified in Article 22 of the Radio Regulations. The current version allows you to consider the "EPFD(down)" interference case in which the interference from the non-GSO satellites into a GSO ground station is evaluated. (more) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Network Traffic Analysis Module
The Network Traffic Analysis Module estimates traffic volume on each link (intersatellite and "ground station-satellite") of a satellite network for a selected routing policy at a given time. (more) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
System Requirements |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Your computer must meet the following requirements: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hardware/Software | Requirements | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Processor | Pentium 1 GHz or faster | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Memory (RAM) | 4 GB or greater | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hard disk space | 100 MB | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monitor resolution | 1280x800 or higher | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Color palette | 16-bit - 32-bit color | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows (64-bit) 11 / 10 / 8.1 / 8 / 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mouse | Microsoft Mouse or compatible pointing device. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| USB Port | Free USB port. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Virtual environment not supported. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||