|
The first two examples were generated with the "Continuous Coverage Constellation Design - Circular Orbits" module. The design requirement was to provide continuous coverage. within -70 ..+70o latitude at a minimum ground elevation angle of 20o. Circular orbits with an altitude of 1400 km have been considered in both cases.
|
|
Click on highlighted links below to see reports produced by the Coverage Analysis and Constraints Analysis modules.
|
|
The Coverage Analysis report shows the minimum number of satellites available at all times to each point of the latitude bound at a given elevation angle (20o). The "P" value in the N field identifies the latitude bound of periodic coverage, "N" - latitude bound, all points of which are never covered by the constellation. The Constraints Analysis report shows the minimum ground elevation angle, which has to be maintained by the generated constellation to provide continuous coverage at specified latitudes.
|
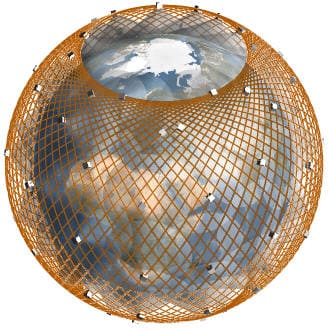
Example 1.1
| Constellation Parameters |
Values |
| Continuous Coverage Area
at a Minimum Elevation Angle of 20o |
-70.75o..+70.75o |
| Number of Satellites |
71 |
| Orbit Inclination (deg) |
121.9 |
| Altitude of Perigee (km) |
1400.0 |
| Altitude of Apogee (km) |
1400.0 |
| Number of Planes |
71 |
| Number of Satellites per Plane |
1 |
| RAAN Increment (deg) |
360.0/71 |
| Phase Increment (deg) |
278.873 |
|
|
|
Example 1.2
| Constellation Parameters |
Values |
| Continuous Coverage Area
at a Minimum Elevation Angle of 20o |
-90.0o..+90.0o |
| Number of Satellites |
70 |
| Orbit Inclination (deg) |
88.0 |
| Altitude of Perigee (km) |
1400.0 |
| Altitude of Apogee (km) |
1400.0 |
| Number of Planes |
7 |
| Number of Satellites per Plane |
10 |
| RAAN Increment (deg) |
27.458 |
| Phase Increment (deg) |
17.011 |
|
|

|
|
Page 1 |
Page 2 |
Page 3 |
Page 4
|
|

